Video Player is loading.
Current Time 0:00
/
Duration 0:00
Loaded: 0%
Stream Type LIVE
Remaining Time -0:00
1x
- 0.5x
- 0.75x
- 1x, selected
- 1.25x
- 1.5x
- 1.75x
- 2x
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
10 seconds
Playback speed
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
1,374 views
January 6, 2013
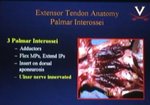
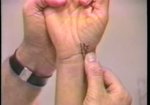
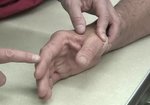
The first test: patient’s hand and especially thumb must be completely relaxed. The examiner applies ...
read more ↘ resistance to the radial surface of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the extended index finger, and the patient actively abducts this finger. The examiner can palpate or even see the strained extensor pollicis brevis tendon.
The second test: patient’s hand and especially thumb must be completely relaxed. The examiner asks the patient to actively extend the small finger. The examiner can palpate or even see the strained extensor pollicis brevis tendon.
↖ read less
read more ↘ resistance to the radial surface of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the extended index finger, and the patient actively abducts this finger. The examiner can palpate or even see the strained extensor pollicis brevis tendon.
The second test: patient’s hand and especially thumb must be completely relaxed. The examiner asks the patient to actively extend the small finger. The examiner can palpate or even see the strained extensor pollicis brevis tendon.
↖ read less
Comments 0
Login to view comments.
Click here to Login