Playback speed
10 seconds
618 views
July 6, 2019
Abstract
Background:
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR) has been established as the gold standard for ...
read more ↘ treatment of complete ruptures of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in active, symptomatic individuals. In contrast, treatment of partial tears of the ACL remains controversial. Biologically augmented ACL-repair techniques are expanding in an attempt to regenerate and improve healing and outcomes of both the native ACL and the reconstructed graft tissue.
Purpose:
To review the biologic treatment options for partial tears of the ACL.
Study Design:
Review.
Methods:
A literature review was performed that included searches of PubMed, Medline, and Cochrane databases using the following keywords: partial tear of the ACL, ACL repair, bone marrow concentrate, growth factors/healing enhancement, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), stem cell therapy.
Results:
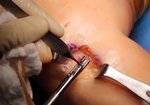
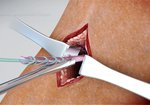
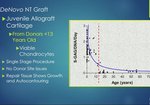
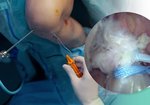
The use of novel biologic ACL repair techniques, including growth factors, PRP, stem cells, and bioscaffolds, have been reported to result in promising preclinical and short-term clinical outcomes.
Conclusion:
The potential benefits of these biological augmentation approaches for partial ACL tears are improved healing, better proprioception, and a faster return to sport and activities of daily living when compared with standard reconstruction procedures. However, long-term studies with larger cohorts of patients and with technique validation are necessary to assess the real effect of these approaches.
↖ read less
Background:
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR) has been established as the gold standard for ...
read more ↘ treatment of complete ruptures of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in active, symptomatic individuals. In contrast, treatment of partial tears of the ACL remains controversial. Biologically augmented ACL-repair techniques are expanding in an attempt to regenerate and improve healing and outcomes of both the native ACL and the reconstructed graft tissue.
Purpose:
To review the biologic treatment options for partial tears of the ACL.
Study Design:
Review.
Methods:
A literature review was performed that included searches of PubMed, Medline, and Cochrane databases using the following keywords: partial tear of the ACL, ACL repair, bone marrow concentrate, growth factors/healing enhancement, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), stem cell therapy.
Results:
The use of novel biologic ACL repair techniques, including growth factors, PRP, stem cells, and bioscaffolds, have been reported to result in promising preclinical and short-term clinical outcomes.
Conclusion:
The potential benefits of these biological augmentation approaches for partial ACL tears are improved healing, better proprioception, and a faster return to sport and activities of daily living when compared with standard reconstruction procedures. However, long-term studies with larger cohorts of patients and with technique validation are necessary to assess the real effect of these approaches.
↖ read less
Login to view comments.
Click here to Login