Video Player is loading.
Current Time 0:00
/
Duration 0:00
Loaded: 0%
0:00
Stream Type LIVE
1x
- 0.5x
- 0.75x
- 1x, selected
- 1.25x
- 1.5x
- 1.75x
- 2x
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
10 seconds
Playback speed
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
Ganglion Cysts of the Wrist
By
Learn MSK Sono
FEATURING
Jamie Bie, RMSKS, RVT, RDMS
By
Learn MSK Sono
FEATURING
Jamie Bie, RMSKS, RVT, RDMS
378 views
June 12, 2023
Do you want to know the most common sites for ganglion cysts of the wrist ...
read more ↘ and how to assess them?
Clinical presentation:
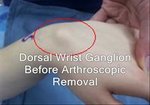
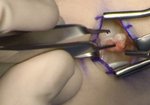
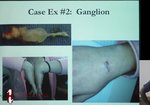
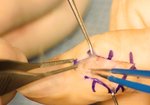
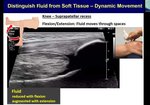
Ganglion cysts commonly occur on both sides of the wrist and will present as a fluid filled palpable lump without a synovial lining. They are often asymptomatic, but can cause pain, deformity in the wrist, and compression of the radial artery or the superficial branch of the radial nerve. Any of these findings may warrant an ultrasound guided aspiration or surgical resection.
Ultrasound appearance:
Simple ganglion cysts appear as avascular, anechoic lesions with posterior acoustic enhancement, but internal echoes or septations may be present.
Location:
🔹 If the patient presents with a cyst on the dorsal surface of the wrist, it typically lies within the joint capsule superficial to the dorsal band of the scapholunate ligament.
🔹 On the other side of the wrist along the volar surface, ganglion cysts usually originate from the scaphotrapezium joint and extend proximally towards the distal radius.
Protocol:
1️⃣ Take grayscale images with and without the surrounding structures labeled
2️⃣ Obtain a volume measurement by obtaining 2 images in the long axis and 1 measurement in the short axis
3️⃣ Use the color doppler images to confirm a lack of vascularity within the cystic lesion and distinguish it from a radial artery pseudoaneurysm
↖ read less
read more ↘ and how to assess them?
Clinical presentation:
Ganglion cysts commonly occur on both sides of the wrist and will present as a fluid filled palpable lump without a synovial lining. They are often asymptomatic, but can cause pain, deformity in the wrist, and compression of the radial artery or the superficial branch of the radial nerve. Any of these findings may warrant an ultrasound guided aspiration or surgical resection.
Ultrasound appearance:
Simple ganglion cysts appear as avascular, anechoic lesions with posterior acoustic enhancement, but internal echoes or septations may be present.
Location:
🔹 If the patient presents with a cyst on the dorsal surface of the wrist, it typically lies within the joint capsule superficial to the dorsal band of the scapholunate ligament.
🔹 On the other side of the wrist along the volar surface, ganglion cysts usually originate from the scaphotrapezium joint and extend proximally towards the distal radius.
Protocol:
1️⃣ Take grayscale images with and without the surrounding structures labeled
2️⃣ Obtain a volume measurement by obtaining 2 images in the long axis and 1 measurement in the short axis
3️⃣ Use the color doppler images to confirm a lack of vascularity within the cystic lesion and distinguish it from a radial artery pseudoaneurysm
↖ read less
Comments 0
Login to view comments.
Click here to Login